Breadcrumb
Blogs
Entries with tag migration .
The Trump Administration’s Newest Migration Policies and Shifting Immigrant Demographics in the USA
New Trump administration migration policies including the "Safe Third Country" agreements signed by the USA, Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras have reduced the number of migrants from the Northern Triangle countries at the southwest US border. As a consequence of this phenomenon and other factors, Mexicans have become once again the main national group of people deemed inadmissible for asylum or apprehended by the US Customs and Border Protection.
![An US Border Patrol agent at the southwest US border [cbp.gov] An US Border Patrol agent at the southwest US border [cbp.gov]](/documents/10174/16849987/migracion-mex-blog.jpg)
▲ An US Border Patrol agent at the southwest US border [cbp.gov]
ARTICLE / Alexandria Casarano Christofellis
On March 31, 2018, the Trump administration cut off aid to the Northern Triangle countries in order to coerce them into implementing new policies to curb illegal migration to the United States. El Salvador, Honduras, and Guatemala all rely heavily on USAid, and had received 118, 181, and 257 million USD in USAid respectively in the 2017 fiscal year.
The US resumed financial aid to the Northern Triangle countries on October 17 of 2019, in the context of the establishment of bilateral negotiations of Safe Third Country agreements with each of the countries, and the implementation of the US Supreme Court’s de facto asylum ban on September 11 of 2019. The Safe Third Country agreements will allow the US to ‘return’ asylum seekers to the countries which they traveled through on their way to the US border (provided that the asylum seekers are not returned to their home countries). The US Supreme Court’s asylum ban similarly requires refugees to apply for and be denied asylum in each of the countries which they pass through before arriving at the US border to apply for asylum. This means that Honduran and Salvadoran refugees would need to apply for and be denied asylum in both Guatemala and Mexico before applying for asylum in the US, and Guatemalan refugees would need to apply for and be denied asylum in Mexico before applying for asylum in the US. This also means that refugees fleeing one of the Northern Triangle countries can be returned to another Northern Triangle country suffering many of the same issues they were fleeing in the first place.
Combined with the Trump administration’s longer-standing “metering” or “Remain in Mexico” policy (Migrant Protection Protocols/MPP), these political developments serve to effectively “push back” the US border. The “Remain in Mexico” policy requires US asylum seekers from Latin America to remain on the Mexican side of the US-Mexico border to wait their turn to be accepted into US territory. Within the past year, the US government has planted significant obstacles in the way of the path of Central American refugees to US asylum, and for better or worse has shifted the burden of the Central American refugee crisis to Mexico and the Central American countries themselves, which are ill-prepared to handle the influx, even in the light of resumed US foreign aid. The new arrangements resemble the EU’s refugee deal with Turkey.
These policy changes are coupled with a shift in US immigration demographics. In August of 2019, Mexico reclaimed its position as the single largest source of unauthorized immigration to the US, having been temporarily surpassed by Guatemala and Honduras in 2018.
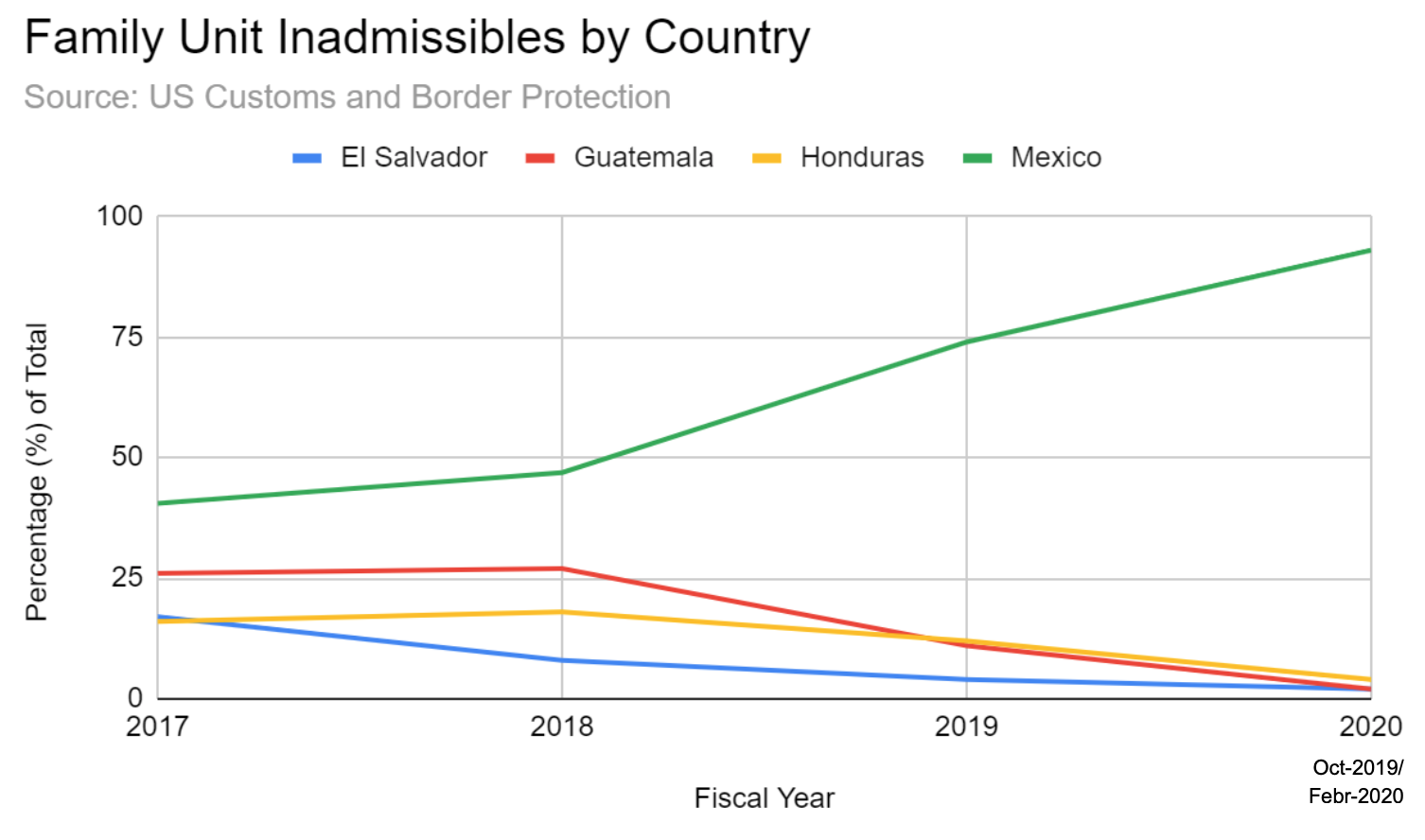
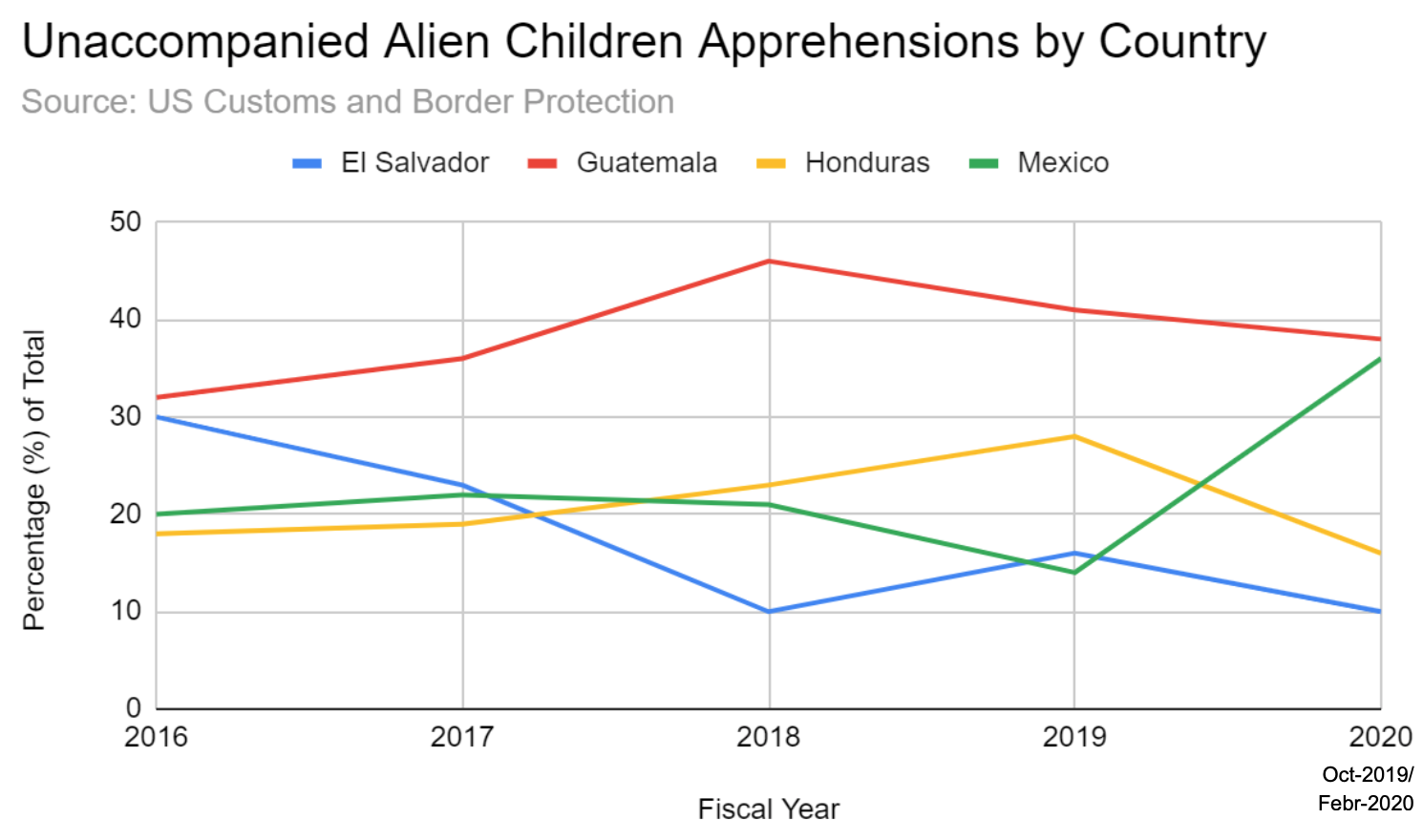
US Customs and Border Protection data indicates a net increase of 21% in the number of Unaccompanied Alien Children from Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador deemed inadmissible for asylum at the Southwest US Border by the US field office between fiscal year 2019 (through February) and fiscal year 2020 (through February). All other inadmissible groups (Family Units, Single Adults, etc.) experienced a net decrease of 18-24% over the same time period. For both the entirety of fiscal year 2019 and fiscal year 2020 through February, Mexicans accounted for 69 and 61% of Unaccompanied Alien Children Inadmisibles at the Southwest US border respectively, whereas previously in fiscal years 2017 and 2018 Mexicans accounted for only 21 and 26% of these same figures, respectively. The percentages of Family Unit Inadmisibles from the Northern Triangle countries have been decreasing since 2018, while the percentage of Family Unit Inadmisibles from Mexico since 2018 has been on the rise.
With asylum made far less accessible to Central Americans in the wake of the Trump administration's new migration policies, the number of Central American inadmisibles is in sharp decline. Conversely, the number of Mexican inadmisibles is on the rise, having nearly tripled over the past three years.
Chain migration factors at play in Mexico may be contributing to this demographic shift. On September 10, 2019, prominent Mexican newspaper El Debate published an article titled “Immigrants Can Avoid Deportation with these Five Documents.” Additionally, The Washington Post cites the testimony of a city official from Michoacan, Mexico, claiming that a local Mexican travel company has begun running a weekly “door-to-door” service line to several US border points of entry, and that hundreds of Mexican citizens have been coming to the municipal offices daily requesting documentation to help them apply for asylum in the US. Word of mouth, press coverage like that found in El Debate, and the commercial exploitation of the Mexican migrant situation have perhaps made migration, and especially the claiming of asylum, more accessible to the Mexican population.
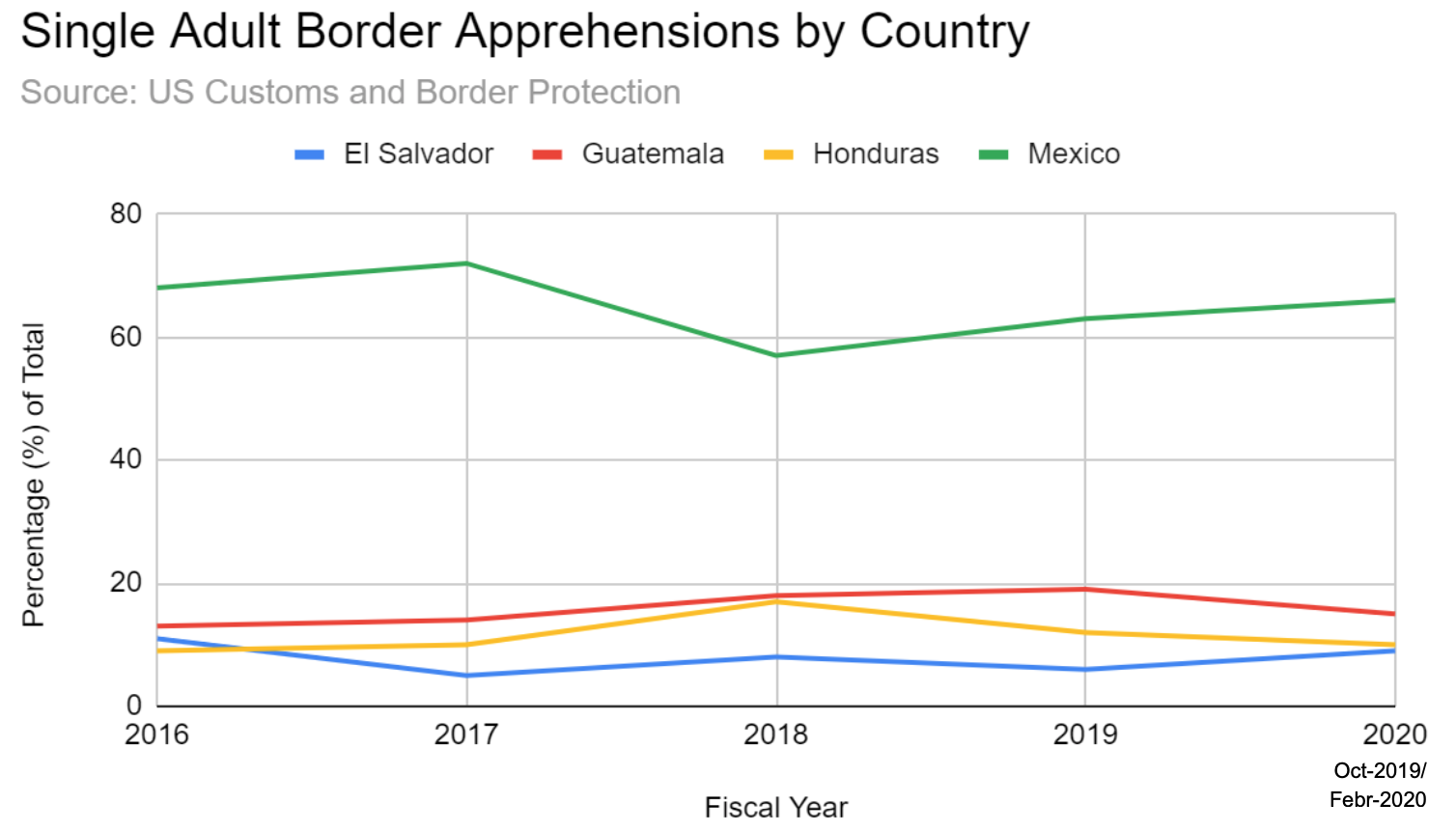
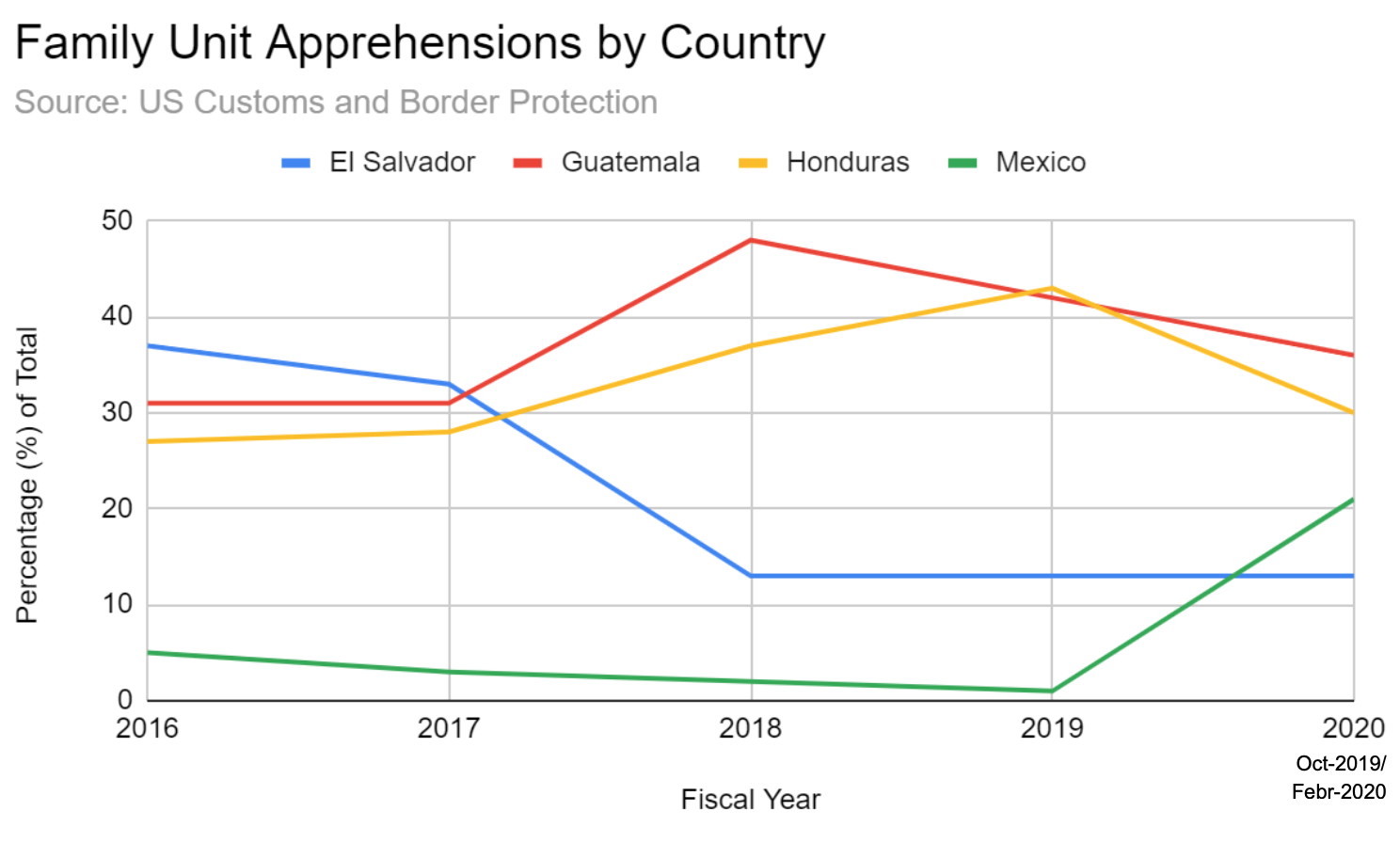
US Customs and Border Protection data also indicates that total apprehensions of migrants from Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador attempting illegal crossings at the Southwest US border declined 44% for Unaccompanied Alien Children and 73% for Family Units between fiscal year 2019 (through February) and fiscal year 2020 (through February), while increasing for Single Adults by 4%. The same data trends show that while Mexicans have consistently accounted for the overwhelming majority of Single Adult Apprehensions since 2016, Family Unit and Unaccompanied Alien Children Apprehensions until the past year were dominated by Central Americans. However, in fiscal year 2020-February, the percentages of Central American Family Unit and Unaccompanied Alien Children Apprehensions have declined while the Mexican percentage has increased significantly. This could be attributed to the Northern Triangle countries’ and especially Mexico’s recent crackdown on the flow of illegal immigration within their own states in response to the same US sanctions and suspension of USAid which led to the Safe Third Country bilateral agreements with Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador.
While the Trump administration’s crackdown on immigration from the Northern Triangle countries has effectively worked to limit both the legal and illegal access of Central Americans to US entry, the Trump administration’s crackdown on immigration from Mexico in the past few years has focused on arresting and deporting illegal Mexican immigrants already living and working within the US borders. Between 2017 and 2018, ICE increased workplace raids to arrest undocumented immigrants by over 400% according to The Independent in the UK. The trend seemed to continue into 2019. President Trump tweeted on June 17, 2019 that “Next week ICE will begin the process of removing the millions of illegal aliens who have illicitly found their way into the United States. They will be removed as fast as they come in.” More deportations could be leading to more attempts at reentry, increasing Mexican migration to the US, and more Mexican Single Adult apprehensions at the Southwest border. The Washington Post alleges that the majority of the Mexican single adults apprehended at the border are previous deportees trying to reenter the country.
Lastly, the steadily increasing violence within the state of Mexico should not be overlooked as a cause for continued migration. Within the past year, violence between the various Mexican cartels has intensified, and murder rates have continued to rise. While the increase in violence alone is not intense enough to solely account for the spike that has recently been seen in Mexican migration to the US, internal violence nethertheless remains an important factor in the Mexican migrant situation. Similarly, widespread poverty in Mexico, recently worsened by a decline in foreign investment in the light of threatened tariffs from the USA, also plays a key role.
In conclusion, the Trump administration’s new migration policies mark an intensification of long-standing nativist tendencies in the US, and pose a potential threat to the human rights of asylum seekers at the US-Mexico border. The corresponding present demographic shift back to Mexican predominance in US immigration is driven not only by the Trump administration’s new migration policies, but also by many other diverse factors within both Mexico and the US, from press coverage to increased deportations to long-standing cartel violence and poverty. In the face of these recent developments, one thing remains clear: the situation south of the Rio Grande is just as complex, nuanced, and constantly evolving as is the situation to the north on Capitol Hill in the USA.
![US border patrol vehicle near the fence with Mexico [Wikimedia Commons] US border patrol vehicle near the fence with Mexico [Wikimedia Commons]](/documents/10174/16849987/us-border-blog.jpg)
▲ US border patrol vehicle near the fence with Mexico [Wikimedia Commons]
ESSAY / Gabriel de Lange
I. Current issues in the Northern Triangle
In recent years, the relationship between the Northern Triangle Countries (NTC) –Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador– and it’s northern neighbours Mexico and the United States has been marked in mainstream media for their surging migration patterns. As of 2019, a total of 977,509 individuals have been apprehended at the Southwest border of the US (the border with Mexico) as compared to 521,093 the previous year (years in terms of US fiscal years). Of this number, an estimated 75% have come from the NTC[1]. These individuals are typically divided into three categories: single adults, family units, and unaccompanied alien children (UAC).
As the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) reports, over 65% of the population of the NTC are below 29 years of age[2]. This is why it is rather alarming to see an increasing number of the youth population from these countries leaving their homes and becoming UAC at the border.
Why are these youths migrating? Many studies normally associate this to “push factors.” The first factor being an increase in insecurity and violence, particularly from transnational organised crime, gangs, and narco-trafficking[3]. It is calculated that six children flee to the US for every ten homicides in the Northern Triangle[4]. The second significant factor is weak governance and corruption; this undermines public trust in the system, worsens the effects of criminal activity, and diverts funds meant to improve infrastructure and social service systems. The third factor is poverty and lack of economic development; for example in Guatemala and Honduras, roughly 60% of people live below the poverty line[5].
The other perspective to explain migration is through what are called “pull factors.” An example would be the lure of economic possibilities abroad, like the high US demand for low-skilled workers, a service that citizens of NTC can provide and be better paid for that in their home countries. Another pull factor worth mentioning is lax immigration laws, if the consequences for illegal entry into a country are light, then individuals are more likely to migrate for the chance at attaining better work, educational, and healthcare opportunities[6].
II. US administrations’ strategies
A. The Obama administration (2008-2015)
The Obama administration for the most part used the carrot and soft power approach in its engagement with the NTC. Its main goals in the region being to “improve security, strengthen governance, and promote economic prosperity in the region”, it saw these developments in the NTC as being in the best interest of US national security[7].
In 2014, in the wake of the massive surge of migrants, specially UACs, the administration launched the reform initiative titled the Plan of the Alliance for Prosperity (A4P). The plan expanded across Central America but with special focus on the NTC. This was a five year plan to address these “push factors” that cause people to migrate. The four main ways that the initiative aims to accomplish this is by promoting the following: first, by fostering the productivity sector to address the region’s economic instability; second, by developing human capital to increase the quality of life, which improves education, healthcare and social services; third, improving citizen security and access to justices to address the insecurity and violence threat, and lastly, strengthening institutions and improving transparency to address the concerns for weak governance and corruption[8].
This initiative would receive direct technical support and financing from the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB). In addition, major funding was to be provided by the US, which for the fiscal years of 2015-2018 committed $2.6 billion split for bilateral assistance, Regional Security Strategy (RSS), and other regional services[9]. The NTC governments themselves were major financiers of the initiative, committing approximately $8.6 billion between 2016-2018[10].
The administration even launched programs with the US Agency for International Development (USAID). The principle one being the Central American Regional Security Initiative (CARSI), with a heavy focus on the NTC and it’s security issues, which allotted a budget of $1.2 billion in 2008. This would later evolve into the larger framework of US Strategy for Engagement in Central America in 2016.
The Obama administration also launched in 2015 the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA), which currently allows individuals who were brought to the US as children, and have unlawful statuses to receive a renewable two-year period of deferred action from deportation[11]. It is a policy that the Trump administration has been fighting to remove these last few years.
Although the Obama administration was quite diplomatic and optimistic in its approach, that didn’t mean it didn’t make efforts to lessen the migration factors in more aggressive ways too. In fact, the administration reportedly deported over three million illegal immigrants through the Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), the highest amount of deportations taking place in the fiscal year of 2012 reaching 409,849 which was higher than any single one of the Trump administration’s reported fiscal years to date[12].
In addition, the Obama administration used educational campaigns to discourage individuals from trying to cross into the US illegally. In 2014 they also launched a Central American Minors (CAM) camp targeting children from the NTC and providing a “safe, legal and orderly alternative to US migration”[13]. This however was later scrapped by the Trump Administration, along with any sense of reassessment brought about by Obama’s carrot approach.
![Number of apprehensions and inadmissibles on the US border with Mexico [Source: CBP] Number of apprehensions and inadmissibles on the US border with Mexico [Source: CBP]](/documents/10174/16849987/us-border-grafico.png)
Number of apprehensions and inadmissibles on the US border with Mexico [Source: CBP]
B. The Trump administration (2016-present)
The Trump administration’s strategy in the region has undoubtedly gone with the stick approach. The infamous “zero tolerance policy” which took place from April-June 2018 is a testimony to this idea, resulting in the separation of thousands of children from their parents and being reclassified as UAC[14]. This was in an attempt to discourage individuals in the NTC from illegally entering the US and address these lax immigration laws.
From early on Trump campaigned based on the idea of placing America’s interests first, and as a result has reevaluated many international treaties and policies. In 2016 the administration proposed scaling back funds for the NTC through the A4P, however this was blocked in Congress and the funds went through albeit in a decreasing value starting with $754 million in 2016 to only $535 million in 2019.
Another significant difference between the two administrations is that while Obama’s focused on large multi-lateral initiatives like the A4P, the Trump administration has elected to focus on a more bilateral approach, one that goes back and forth between cooperation and threats, to compliment the existing strategy.
Towards the end of 2018 the US and Mexico had announced the concept of a “Marshal Plan” for Central America with both countries proposing large sums of money to be given annually to help improve the economic and security conditions in the NTC. However in this last year it has become more apparent that there will be difficulties raising funds, especially due to their reliance on private investment organisations and lack of executive cooperation. Just last May, Trump threatened to place tariffs on Mexico due to its inability to decrease immigration flow. President López Obrador responded by deploying the National Guard to Mexico’s border with Guatemala, resulting in a decrease of border apprehensions by 56%[15] on the US Southwest border. This shows that the stick method can achieve results, but that real cooperation can not be achieved if leaders don’t see eye to eye and follow through on commitments. If large amount of funding where to be put in vague unclear programs and goals in the NTC, it is likely to end up in the wrong hands due to corruption[16].
In terms of bilateral agreements with NTC countries, Trump has been successful in negotiation with Guatemala and Honduras in signing asylum cooperative agreements, which has many similarities with a safe third country agreement, though not exactly worded as such. Trump struck a similar deal with El Salvador, though sweetened it by granting a solution for over 200,000 Salvadorans living in US under a Temporary Protection Status (TPS).[17]
However, Trump has not been the only interested party in the NTC and Mexico. The United Nations’ ECLAC launched last year its “El Salvador-Guatemala-Honduras-Mexico Comprehensive Development Program”, which aims to target the root causes of migration in the NTC. It does this by promoting policies that relate to the UN 2030 agenda and the 17 sustainable development goals. The four pillars of this initiative being: economic development, social well-being, environmental sustainability, and comprehensive management of migratory patters[18]. However the financing behind this initiative remains ambiguous and the goals behind it seem redundant. They reflect the same goals established by the A4P, just simply under a different entity.
The main difference between the Obama and Trump administrations is that the A4P takes a slow approach aiming to address the fundamental issues triggering migration patterns, the results of which will likely take 10-15 years and steady multi-lateral investment to see real progress. Meanwhile the Trump administration aims to get quick results by creating bilateral agreements with these NTC in order to distribute the negative effects of migration among them and lifting the immediate burden. Separately, neither strategy appears wholesome and convincing enough to rally congressional and public support. However, the combination of all initiatives –investing effort both in the long and short run, along with additional initiatives like ECLAC’s program to reinforce the region’s goals– could perhaps be the most effective mechanism to combat insecurity, weak governance, and economic hardships in the NTC.
[1] Nowrasteh, Alex. “1.3 Percent of All Central Americans in the Northern Triangle Were Apprehended by Border Patrol This Fiscal Year - So Far”. Cato at Library. June 7, 2019. Accessed November 8, 2019.
[2] N/A. “Triángulo Norte: Construyendo Confianza, Creando Oportunidades.” Inter-American Development Bank. Accessed November 5, 2019.
[3] Orozco, Manuel. “Central American Migration: Current Changes and Development Implications.” The Dialogue. November 2018. Accessed November 2019.
[4] Bell, Caroline. “Where is the Northern Triangle?” The Borgen Project. October 23, 2019. Accessed November 6, 2019.
[5] Cheatham, Amelia. “Central America’s Turbulent Northern Triangle.” Council on Foreign Relations. October 1, 2019. Accessed November 6, 2019.
[6] Arthur, R. Andrew. “Unaccompanied Alien Children and the Crisis at the Border.” Center for Immigration Studies. April 1, 2019. Accessed November 9, 2019.
[7] Members and Committees of Congress. “U.S. Strategy for Engagement in Central America: Policy Issues for Congress.” Congressional Research Service. Updated November 12, 2019. November 13, 2019.
[8] N/A. “Strategic Pillars and Lines of Action.” Inter-American Development Bank. 2019. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[9] N/A. “Budgetary Resources Allocated for the Plan of the Alliance for Prosperity.” Inter-American Development Bank. N/A. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[10] Schneider, L. Mark. Matera, A. Michael. “Where Are the Northern Triangle Countries Headed? And What Is U.S. Policy?” Centre for Strategic and International Studies. August 20, 2019. Accessed November 11, 2019.
[11] N/A. “Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA).” Department of Homeland Security. N/A. Accessed November 12, 2019.
[12] Kight, W. Stef. Treene, Alayna. “Trump isn’t Matching Obama deportation numbers.” Axios. June 21, 2019. Accessed November 13, 2019.
[13] N/A. “Unaccompanied Alien Children: An Overview.” Congressional Research Service. October 9, 2019. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[14] N/A. “Unaccompanied Alien Children: An Overview.” Congressional Research Service. October 9, 2019. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[15] Nagovitch, Paola. “Explainer: U.S. Immigration Deals with Northern Triangle Countries and Mexico.” American Society/Council of Americans. October 3, 2019. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[16] Berg, C. Ryan. “A Central American Martial Plan Won’t Work.” Foreign Policy. March 5, 2019. Accessed November 11, 2019.
[17] Nagovitch, Paola. “Explainer: U.S. Immigration Deals with Northern Triangle Countries and Mexico.” American Society/Council of Americans. October 3, 2019. Accessed November 10, 2019.
[18] Press Release. “El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras and Mexico Reaffirm their Commitment to the Comprehensive Development Plan.” ECLAC. September 19,2019. Accessed November 11, 2019.
The avalanche of unaccompanied foreign minors suffered by the Obama administration in 2014 has been overcome in 2019 by a new immigration peak
In the summer of 2014, the United States suffered a migration crisis due to an unexpected increase in the number of unaccompanied foreign minors, mostly Central Americans, who arrived at its border with Mexico. What has happened since then? Although oscillating, the volume of this type of immigration fell, but in 2019 a new record has been registered in the wake of the recent “caravan crisis”, which has increased again total apprehensions on the border.
![US Customs and Border Protection agents processing unaccompanied children, in Texas, at the border with Mexico, in 2014 [Hector Silva, USCBP–Wikimedia Commons] US Customs and Border Protection agents processing unaccompanied children, in Texas, at the border with Mexico, in 2014 [Hector Silva, USCBP–Wikimedia Commons]](/documents/10174/16849987/migracion-blog.jpg)
▲ US Customs and Border Protection agents processing unaccompanied children, in Texas, at the border with Mexico, in 2014 [Hector Silva, USCBP–Wikimedia Commons]
ARTICLE / Marcelina Kropiwnicka [Spanish version]
The United States hosts more immigrants than any other country in the world, with more than one million people arriving every year either as permanent legal residents, asylum-seekers and refugees, or in other immigration categories. While there is no official measure of tracking how many people successfully cross the border illegally, US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) authorities measure the changes in illicit immigration using the amount of apprehensions per fiscal year; apprehensions being an indicator of total attempts to cross the border illegally. Looking at data, it can be concluded that there have been notable changes in the demographics of illegal migration on the southwest border with Mexico (or Southwest border) over the last few years.
The soaring peak of apprehensions on the Southwest border was in 2000 when 1.64 million persons were detained for trying to enter the US illegally. The figures have generally declined since. Interestingly enough, in recent years, there has been more overall seizures of non-Mexicans than Mexicans at US borders, reflecting a decline in the number of unauthorized Mexican immigrants coming to the US over the past decade. The surge, in fact, was largely due to those fleeing violence, gang activity and poverty in Guatemala, Honduras and El Salvador, known collectively as the Northern Triangle.
The nations included in the Northern Triangle are among the poorest in Latin America—a high percentage of the population still lives on less than $2 a day (the international poverty line is $1.90)—with minimal advancement occurring to reduce poverty in recent years. Within Latin America and the Caribbean, Honduras has the second-highest share with 17% of the population living below the international poverty line, after Haiti, according to the latest data from the World Bank.
Unaccompanied Alien Children
Far fewer single adults have been attempting to cross the border without authorization over the past decade, and a surge of unaccompanied alien children (UAC) crossing the Southwest border occurred. The migration of minors without an adult is not new; the novelty today is the size of this migration and the generation of policies in response to the issue. The spike of UAC apprehensions in FY2014 caused alarm and prompted media scrutiny and policy responses, and attention remained even as the number decreased; numbers dropped back down to just under 40,000 UAC apprehensions the following year.
The international community defines an unaccompanied migrant child as a person, “who is under the age of eighteen” and who is “separated from both parents and is not being cared for by an adult who by law or custom has responsibility to do so” (UNHCR 1997). Many of these unaccompanied children immediately present themselves to US-border security whereas others enter the US unnoticed and undocumented. Not only this, the children have no parent or legal guardian available to provide care or physical custody which swiftly overwhelms local border patrols.
In 2014, many of the unaccompanied children claimed they were under the false impression that the Obama Administration was granting "permisos" to children who had family members in the US, as long as they arrived by June. These false claims and “sales pitches” have become more potent this past year, especially when President Trump continues to reinforce the idea of restricting migrant access to the US. Cartels have continued transporting soaring numbers of Central American migrants from their countries to the United States.
Critical moments of 2014 and 2019
During Obama’s second term, in FY2014, total apprehensions along the Southwest border reached the number of 569.237 (the figure includes "inadmissibles"), a record only surpassed now. The apprehensions soared 13% compared to FY2013, but the main increase was for UAC seizures, which surged immensely from 38,759 in FY2013 to 68,541 in FY2014, a nearly 80% increase, as well as more than four times as many UAC as in FY2011. In a year, the figure of minors from Honduras increased from 6,747 to 18,244; minors from Guatemala rose from 8,068 to 17,057, and those from El Salvador, from 5,990 to 16,404 (minors from Mexico, on the other hand, dropped from 17,240 to 15,634). Apprehensions were highest along the Southwest border in the month of May, where 17% was made up by UAC seizures.
Since FY2014, UAC apprehensions have fluctuated considerably. In FY2019, however, apprehensions of UAC reached 76,020, a level that now exceeds the peak reached in FY2014. The maximum level was registered in May; however, that month they accounted for only 9% of total apprehensions, because this time it was not properly a UAC crisis, but a remarkable peak of total apprehensions. Although general apprehensions decreased significantly during the first six months of Trump’s tenure, they rose alarmingly in FY2019, reaching a total of 851,508 (977,509 if the "inadmissibles" are added). Current data shows that seizures along the Southwest border have more than doubled from the previous FY2018. The number of overall apprehensions increased by 72% from FY2014 to FY2019 (in the case of UAC increased 11%).
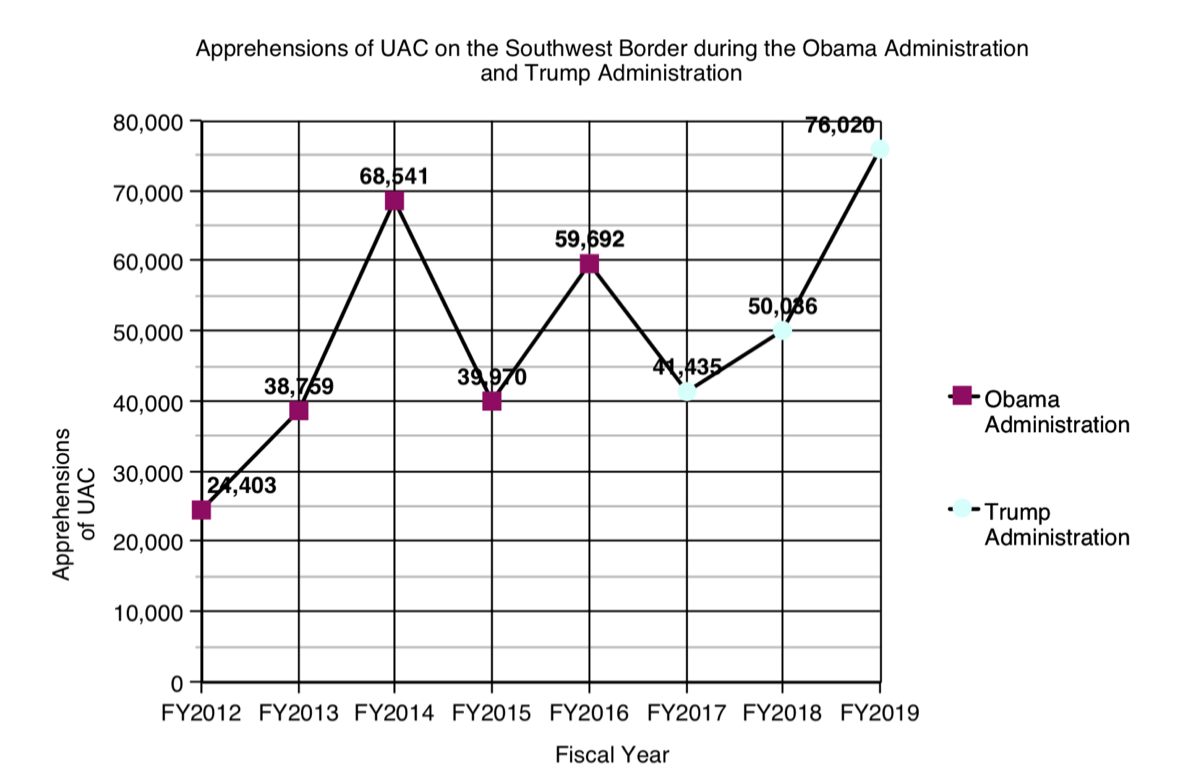 |
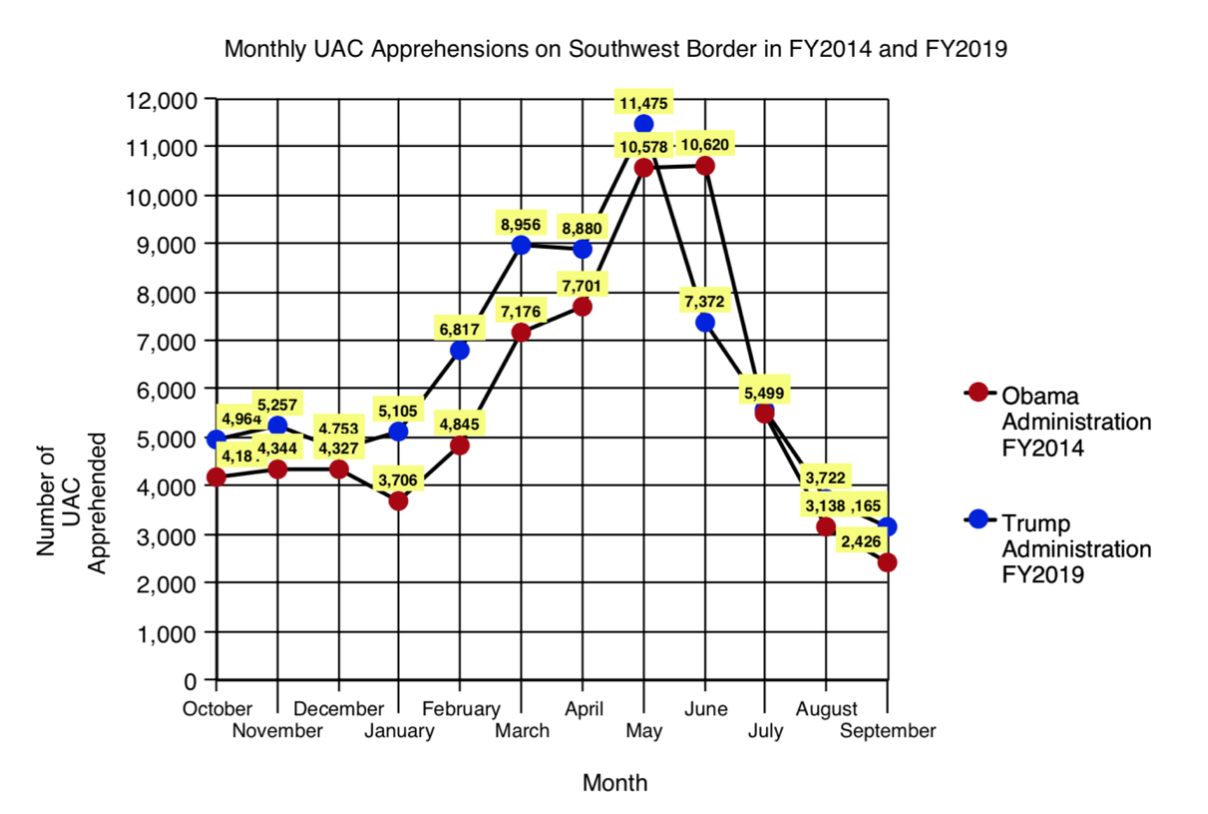 |
Apprehensions of Unaccompanied Alien Children on the US-México border, between 2012 and 2019 (figure 1), and comparison between 2014 and 2019 by month (figure 2). Source: US Customs and Border Patrol.
US Policies
The US had established numerous domestic policies which dealt with the massive rise in immigration. With the overwhelming peak in 2014, however, Obama requested funding for "the repatriation and reintegration of migrants to countries in Central America and to address the root causes of migration from these countries". Though funding was fairly consistent the past years for the program, the budget for FY2018 proposed by President Trump would cut aid to these countries by approximately 30%.
While Trump’s administration has made notable progress in its immigration agenda, from beginning the construction of the wall to enforcing new programs, the hardline policies that were promised before inauguration have thus far been unsuccessful in stopping thousands of Central American families from trekking across the Southern Border into the US. With extreme gang violence being rampant and the existence of “loopholes” in the US immigration system, the pull-factor for migrants will remain.
ESSAY / Marina Díaz Escudero
Since 2015, Europe has been dealing with an unprecedented scale of migration from different parts of the world, mainly from MENA (Middle East and North Africa). People flee their countries due to war, bad living conditions or a lack of opportunities for wellbeing.
Although Europe characterises itself for its solidarity, liberty, values and respect for other countries and cultures, such a large flow of inmigration seriously tests the European project. For instance, the Schengen system of passport-free travel could collapse as fearful countries enhance their border controls, to the disadvantage of European citizens. “The Schengen system is being more and more questioned and most opinion polls highlight the correlation between the fear of inmigration and the distrust of the citizens of the member states towards European institutions.”1 The migration crisis is also considered a “threat for the European project’s constitutional stability and for its fundamental values” (Spijkerboer, 2016). 1
Divisions between northern and southern EU countries, and between them and the Visegrad countries have clearly intensified due to this problem, specially after the approval, in 2015, of some quotas of relocation of refugees that were critisised and voted against by Hungary, the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Due to this lack of consensus but also due to the delay of other EU countries in complying with the quotas, a treaty was signed between the EU and Turkey in March 2016 so that most refugees arriving to Europe through Greece would be inmediately returned to Turkey2.
Understandably, EU countries are mostly concerned with the prevention of illegal inmigration and with border-control policies, as well as with the need of reaching an agreement for an egalitarian distribution of arriving migrants, most of them being asylym seekers and refugees. Nevertheless, this will probably not be enough to satisfy both the European citizens and the migrants: root causes of migration may need to be solved as soon as possible to prevent people from fleeing their homes. This gives the EU food for thought: addressing the migration problem without focusing on the prevention of migration in the countries of origin may not be a lasting, long-term solution. “The instability, insecurity, terrorism, poverty, famine and climate change besetting large parts of Africa and the Middle East are the root causes of migration, but the European Union (EU) governments have come around to this too late, engaging essentially in damage-limitation exercises at our borders.”3
According to World Bank data, in 2017 over 8 million migrants came from “the Arab world” and from these, 6 million fleed the Syrian Arab Republic4. The war in Syria, originally between Bashar al Assad’s regime and the rebel opposition, and currently a proxy war involving various international actors, turns the country into one of the greatest sources of migrants. The fact that over a million of them live in Lebanon (currently accounting for a 30% of the population) , a country who didn’t sign the 1951 Refugee Convention and who has been trying to deport the migrants for years now, is worrying. Due to the “fuelling tensions between Lebanese host communities and the Syrian refugees” the Lebanese government has taken some more restrictive measures towards migrants, such as the banning of the construction of formal refugee camps. This for sure puts additional pressure on the EU5.
In order to comprehend the European Union’s vision and strategy on Syria, and whether the institution and its members are willing to fight the root causes of its situation, one must consider the words of the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, Federica Mogherini, in her discourse at the Conference of Brussels in April 2018:
“[In this conference] we had representatives of over 85 countries and international organizations, international and Syrian civil society. […] We identified common ground on at least 2 or 3 issues: one is that there is no military solution to the war in Syria and that there is a need that everyone recognizes to relaunch the political process. The second element on which I have not found any divergent view is the key role of the United Nations in leading this political process. This is extremely important for us, the European Union, because we have always consistently identified in the UN and in Staffa de Mistura the only legitimate leadership to ensure that the political process represents all Syrians in intra-Syrian talks and happens along the lines of the United Nations Security Council resolutions already adopted. The third element is the need to support Syrians inside Syria and in the neighbouring countries, with humanitarian aid, financial support but also to support hosting communities, in particular neighbouring countries”.6
The Vice-President of the European Comission basically makes three clear statements: the European institution will by no means intervene militarily in Syria, neither will it take the initiative to start a political process or peaceful negotiation in the country (it will only support the UN-led process), but it will clearly invest economically both in the country and in its citizens to improve their conditions.
Defence of the UN-led political process
Once a solely-European military intervention has been discarded (due to a lack of consensus among countries on a common defense policy and to the already effective existence of NATO in this regard), the EU considers its role in a political solution to the Syrian conflict, which would clearly reduce migration numbers.
According to the European Council in its conclusions on Syria of April 2018, “the momentum of the current situation should be used to reinvigorate the process to find a political resolution of the Syrian conflict […] A lasting peace in Syria is the ultimate objective of the EU”.7 The Council makes clear that it will not create a new EU-led political process but that it will support the UN’s: “…any sustainable solution to the conflict requires a genuine political transition in line with UNSCR 2254 and the 2012 Geneva Communique negotiated by the Syrian parties within the UN-led Geneva process.”
The UN currently takes part in two parallel processes: inter-Syrian conversations in Geneva and the Conversations in Astaná. The first looks for a dialogue solution to the conflict and participants are the Syrian government, a delegation from the opposition and the UN Special Envoy for Syria. Until now, 9 rounds of conversations have taken place, the last focused on the elaboration of a new constitution for the country. The second process is promoted by Russia, Iran and Turkey, guarantors of the peace process in Syria. Conversations started in 2017 with the aim of consolidating the cease-fire and preparing the way for a political solution to the war. The last round of conversations took place in Sochi this past July8.
But things aren’t as easy as they seem.
UN special envoy for Syria will soon be replaced by the Norwegian Geir Pedersen making future lines of action unpredictable for us. We know, however, what the starting point will be. In the ordinary UN session celebrated on the past 20th december, de Mistura stated that they had “almost completed the job of starting a constitutional commitee to write a constituional reform, as a contribution to the political process, but still have to go one more mile.”9
Such a commiteee would be composed of 150 persons, a third of which should be appointed by the Syrian regime, another third by the opposition and the last one by UN designated persons. This last point has been repeatedly opposed by Syria. The biggest problem at the moment is that the UN is not fully comfortable with the 50-name list proposed by Iran, Russia and Turkey9.
On the other hand, the strategy of the US, a very relevant actor in this process due to its position in the UN as a permanent member of the Security Council (with veto power on resolutions), has been unclear for a long time. US Special Envoy to Syria Joel Rayburn stated in November that the objectives of the US in Syria were three: the defeat of the Islamic State, the withdrawal of all Iranian-commanded forces and “a political settlement under the auspices of the UNSC Resolution 2254 and the political process supported by the UN in Geneva.”10
In other words, it seemed that unless the first two objectives were covered the US wouldn’t wholeheartedly compromise for a definitive political settlement in Syria and given US relevance, the UN would have it very difficult to advance the political process anytime soon. Most recently however, there was a turn of events: in December the US declared its intention of gradually withdrawing its troops from Syria. “We have defeated ISIS in Syria, my only reason for being there during the Trump presidency.”11
Does this mean that the US is finally willing to head its efforts towards the third objective? US diplomat Rodney Hunter said: “the US is ready to impulse the political process, to isolate more the regime diplomatic and economically, we are willing to do it.” 9
Although a positive answer would facilitate discussions for peace and thus, EU involvement, a reduction of violence in the region (and therefore a reduction of migration to Europe) is not assured for two reasons: the US now leaves Turks with free hands to attack Kurdish militants and, although ISIS has lost 95% of its territory, “2,500 Isis fighters remain […] The group retains the capacity to do even more damage, especially if let off the hook now.” 11
Soft power: humanitarian aid and investment
Given the fact that the EU can not really influence the military and political/diplomatic decisions regarding the Syrian conflict, it has been focusing, since the beginning of the war in 2011, on delivering humanitarian aid and development support to the country and its nationals. The next phrase from the European External Action Service summarises very well the EU’s aims on this respect: “Our objective is to bring an end to the conflict and enable the Syrian people to live in peace in their own country.”12
Although bilateral, regional and technical assitance cooperation between the EU and the Syrian government came to an end due to the violent situation that was emerging in the country, the international organization directly supports the Syrian population and its neighbours13.
Through the European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP), the EU worked hand in hand with its neighbours to the East and South (including Syria) with the aim of fostering stabilization, security and prosperity and achieving cooperation in key areas like the “promotion of democracy, rule of law, respect for human rights and social cohesion.”14 After the cease of cooperation between the EU and the regime, support to the ENP countries is given through the European Neighbourhood Instrument (ENI), with a predicted budget of 15 billion dollars (2014-2020)15.
Under the financing og the ENI, the Commission approved in November a special measure “to help the Syrian population to cope with the effects of the crisis and prepare the grounds for a sustainable peace.”16 The main action has been entitled as “Preserving the prospects for peace and stability in Syria through an inclusive transition” and counts with a maximum contribution of EUR 31 million. According to the European Comission, if the Syrian situation turns into a “post-crisis state-building and reconstruction scenario,” special measures will be revised in order to suit the new needs of the population14.
The ENP is part of the EUGS or European Union Global Strategy (for the European Union’s Foreign and Security Policy) presented by Federica Mogherini to the EU Council in 2016, and whose main aim is to achieve an integrated approach and a “coherent perspective for EU’s external action.”15 As part of this broader strategy, the EU wishes to prevent fragile contexts from becoming serious humanitarian crises17.
Within this, another particular strategy for Syria was developed in 2015, the EU Strategy for Syria. Some of its most important objectives are “saving lives by addressing the humanitarian needs of the most vulnerable Syrians across the country,” “promoting democracy, human rights and freedom of speech by strengthening Syrian civil society organisations” and “support the resilience of the Syrian population and Syrian society.”18 The European Council, in its Conclusions on Syria of 2018, agreed that the objectives of the “European Union Strategy on Syria” remain valid.
Although all these initiatives are well-intentioned and show that the EU is not only concerned about the end of the war but also with how it will be done and its aftermath, history has proved that Western political intervention in the Middle East is far from optimum for the region. In the 1916 the Sykes-Picot agreement between France and the UK drew an artificial political line on the territory that would later trigger the Arab-Israeli conflict and promote present ISIS action. Later on, the US-leaded intervention in Iraq in 2003 (one of its objectives being the “liberation” of the Iraqi people) has caused an increase of Sunni-Shiite tension, the rise of Al-Qaeda and the strenghtening of Iran in the region.
The point here is that the EU might be interested in helping Syria and its citizens in ways that improve living conditions and welfare opportunities without messing up with the country’s cultural, social and political system. Imposing the notion of democracy in these states, knowing that they have a completely different historical and cultural background, might not be a feasible solution.
Thus, other types of EU initiatives like the New Partnership Framework (NPF, June 2016), focused on the role of economic development in fighting the root causes of migration, might be more effective in the long-term. “It will address all aspects of this migration crisis, from its root causes to the daily tragedies that occur in the Mediterranean. These ambitions […] illustrate EU's willingness to address specific migratory challenges, but also the long-term drivers of migration.”19
Through the NPF, the EU explains how private investment can be a very useful tool for promoting the economic growth and development of Syria, which would in turn improve the living conditions of its citizens making it less necessary to flee their homes in search of a better place to be. “Instead of letting irregular migrants risk their lives trying to reach European labour markets, European private and public resources should be mobilised for investment in third countries of origin. If deployed intelligently, leveraged use of the limited budget resources available will generate growth and employment opportunities in source as well as transit countries and regions […] This should adress the root causes of migration directly, given the high impact of those investments in terms of employment and inequality reduction.” This is what the EU calls innovative financing mechanisms.
This project is called the External Investment Plan and is being organized in three steps. First, the mobilization of scarce public resources in an attractive way to attract private investment. Then, helping local authorities and private companies to be known in the international investor community. Finally, the EU would try to improve the general business government by putting a solution to some corruption issues as well as some market distortions. “The EU, Member States, third countries, International Financial Institutions, European bilateral development institutions, as well as the private sector, should all contribute.” The EU hopes to collect, through this External Investment Fund, a total of 62 billion euros.
Long story short, European countries believe in the expansion of this type of innovative financing “in those fragile and post-conflict countries which are often important for migration flows but where the potential for direct private or public investment is currently limited.”
An interesting factor to take into account in this matter is who will be the most involved international actor in the project. Will it be the US, allowing us to compare the current situation with the 20th century Marshall Plan? (where investments in infrastructure and the spread of domestic management techniques was also a key element). Or could it be Russia? As the President of the Russian Chamber of Commerce stated in March 2018, “$200 billion to $500 billion will be needed for the reconstruction of the Syrian economy, and the first priority will, as President Bashar al-Assad has said, be given to Russian businesses.”20 What is clear is that investing in Syria will clearly give the investor country some important influence on the newly-recovered state.
Conclusions and forecast for the future
Since the beginning of the crisis in 2011, Syria has been one of the major sources of migration towards Europe. Although EU members currently need to discuss the prevention of illegal inmigration and the distribution of legally coming asylum seekers, some attention must also be given to the elimination of factors that activate migration in the country of origin.
While it is true that a definitive end to the war between the regime and the opposition would be the best and most inmediate solution for disproportionate fleeings from Syria, the EU doesn’t seem to be able to intervene more than it already does.
Not having an army of itself (and not seeming to want it in the near future) and being the “assistant” of the UN in the political and diplomatic resolution of the conflict, it can only apply its soft power tools and instruments to help to the country and its citizens.
Although humanitarian aid is essential and the EU is sparing no expense on it, the institution has come to realise that the real key to improving Syria’s situation and the wellbeing of its citizens may be investment and development. This investment could be “short-term”, in the sense that foreign countries directly invest in Syria and decide what the money will be used for (i.e reconstruction of buildings, construction of new infrastructure…) or “long-term”, in the sense that the main role of the EU is improving the country’s business governance to facilitate the attraction of private investors in the long-term.
Regarding the last option it is very important that “the receptor countries establish transparent policies, broad and effective that propiciate an appropiate atmosphere for investment, with the consequent formation of human resources and the establishment of an appropiate institutional climate.”21 Taking this into account, Syria will be a difficult challenge for the EU, as in order to achieve an appropiate institutional climate, a diplomatic solution to the conflict and a peaceful political transition will be required, as well as the collaboration of the future government in promoting political transparency.
All in all, the EU is clearly aware of the root causes of migration and is developing feasible strategies to counter them. The rate of progress is still slow and it may be due to the fact that, in order to effectively apply many of this soft power strategies (except for the humanitarian aid), the receptor country must be stable and ready to collaborate. In other words, EU investment and development plans will most probably bear fruit when the war is over, a peaceful political transition is on the move and the general atmosphere is favourable for economic growth and innovation.
Political stability in Syria could be achieved through two scenarios: the success of the UN-led process and the drafting of new constitution for the country; or the victory of one of the sides (most probably the Syrian regime) and its establishment in power. Meanwhile, the EU and its members will have three challenges: developping the forementioned long-term investment strategies in the view of a future peace (while mantaining already-functioning soft power initiatives), dealing with the refugee crisis at the European borders, and preserving the European project and unity by avoiding major disagreements on migration policy and an exacerbated fear of inmigration.
Moreover, one of the key issues that will need to be followed closely in the following months is the effect that the, maybe early, withdrawal of US troops can have on the region and on the power dynamic between the actors, together with the potential changes in US strategy with regards to the UN-led process.
References
-
CIDOB - «Inmigración y asilo: en el centro de la arena política». Anuario CIDOB de la Inmigración 2018. (2018). Retrieved from
-
López, E. (2018). Refugee crisis: The divergence between the European Union and the Visegrad Group/ GLOBAL AFFAIRS, UNAV. Retrieved from
-
Tajani, A. (2018). The migration crisis threatens to destroy the EU. We must not let it | Antonio Tajani. Retrieved from
-
Refugee population by country or territory of origin | Data. (2017). Retrieved from
-
Lebanon - European Civil Protection and Humanitarian Aid Operations - European Commission. (2019). Retrieved from
-
Photos and videos of the conference - Consilium. (2018). Retrieved from
-
Battu, V. (2018). Syria: Council adopts conclusions - Consilium. Retrieved from
-
Siria. Retrieved from
-
La ONU sigue atascada para una solución en Siria, mientras EE.UU. anuncia su retirada. (2018). Retrieved from
-
Elgeneidy, S. (2018). INTERVIEW: ‘We need a political settlement of the conflict’, US Special Envoy to Syria says - Region - World - Ahram Online. Retrieved from
-
Chulov, M. (2018). Has Isis been defeated in Syria, as Trump claims?. Retrieved from
-
Syria and the EU - EEAS - European External Action Service - European Commission. (2016). Retrieved from
-
Syria - European Neighbourhood Policy And Enlargement Negotiations - European Commission. (2018). Retrieved from
-
European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP) - Commission européenne. (2016). Retrieved from
-
European Neighbourhood Policy - European Neighbourhood Policy And Enlargement Negotiations - European Commission. (2018). Retrieved from
-
Comission implementing decision on the special measure in favour of the Syrian population for 2018. (2018). Retrieved from
-
EUGS at 1 - EU Global Strategy - European Commission. (2019). Retrieved from
-
Battu, V. (2017). Council adopts EU strategy on Syria - Consilium. Retrieved from
-
Communication on establishing a new Partnership Framework with third countries under the European Agenda on Migration. (2016). Retrieved from
-
"Russian business first in line for spoils of Syrian war/Subscribe to read | Financial Times. Retrieved from
-
Foreign Direct Investment for Development: Maximising Benefits, Minimising Costs. (2002). Retrieved from
