
IDF soldiers during a study tour as part of Sunday culture, at the Ramon Crater Visitor Center [IDF]
ESSAY / Jairo Císcar
The geopolitical reality that exists in the Middle East and the Eastern Mediterranean is incredibly complex, and within it the Arab-Israeli conflict stands out. If we pay attention to History, we can see that it is by no means a new conflict (outside its form): it can be traced back to more than 3,100 years ago. It is a land that has been permanently disputed; despite being the vast majority of it desert and very hostile to humans, it has been coveted and settled by multiple peoples and civilizations. The disputed territory, which stretches across what today is Israel, Palestine, and parts of Lebanon, Jordan, Egypt, and Syria practically coincides with historic Canaan, the Promised Land of the Jewish people. Since those days, the control and prevalence of human groups over the territory was linked to military superiority, as the conflict was always latent. The presence of military, violence and conflict has been a constant aspect of societies established in the area; and, with geography and history, is fundamental to understand the current conflict and the functioning of the Israeli society.
As we have said, a priori it does not have great reasons for a fierce fight for the territory, but the reality is different: the disputed area is one of the key places in the geostrategy of the western and eastern world. This thin strip, between the Tigris and Euphrates (the Fertile Crescent, considered the cradle of the first civilizations) and the mouth of the Nile, although it does not enjoy great water or natural resources, is an area of high strategic value: it acts as a bridge between Africa, Asia and the Mediterranean (with Europe by sea). It is also a sacred place for the three great monotheistic religions of the world, Judaism, Christianity and Islam, the “Peoples of the Book”, who group under their creeds more than half of the world's inhabitants. Thus, for millennia, the land of Israel has been abuzz with cultural and religious exchanges ... and of course, struggles for its control.
According to the Bible, the main para-historical account of these events, the first Israelites began to arrive in the Canaanite lands around 2000 BC, after God promised Abraham that land “... To your descendants ...”[1] The massive arrival of Israelites would occur around 1400 BC, where they started a series of campaigns and expelled or assimilated the various Canaanite peoples such as the Philistines (of which the Palestinians claim to be descendants), until the Kingdoms of Israel and Judah finally united around the year 1000 BC under a monarchy that would come to dominate the region until their separation in 924 BC.
It is at this time that we can begin to speak of a people of Israel, who will inhabit this land uninterruptedly, under the rule of other great empires such as the Assyrian, the Babylonian, and the Macedonian, to finally end their existence under the Roman Empire. It is in 63 BC when Pompey conquered Jerusalem and occupied Judea, ending the freedom of the people of Israel. It will be in 70 AD, though, with the emperor Titus, when after a new Hebrew uprising the Second Temple of Jerusalem was razed, and the Diaspora of the Hebrew people began; that is, their emigration to other places across the East and West, living in small communities in which, suffering constant persecutions, they continued with their minds set on a future return to their “Promised Land”. The population vacuum left by the Diaspora was then filled again by peoples present in the area, as well as by Arabs.
The current state of Israel
This review of the historical antiquity of the conflict is necessary because this is one with some very special characteristics: practically no other conflict is justified before such extremes by both parties with “sentimental” or dubious “legal” reasons.
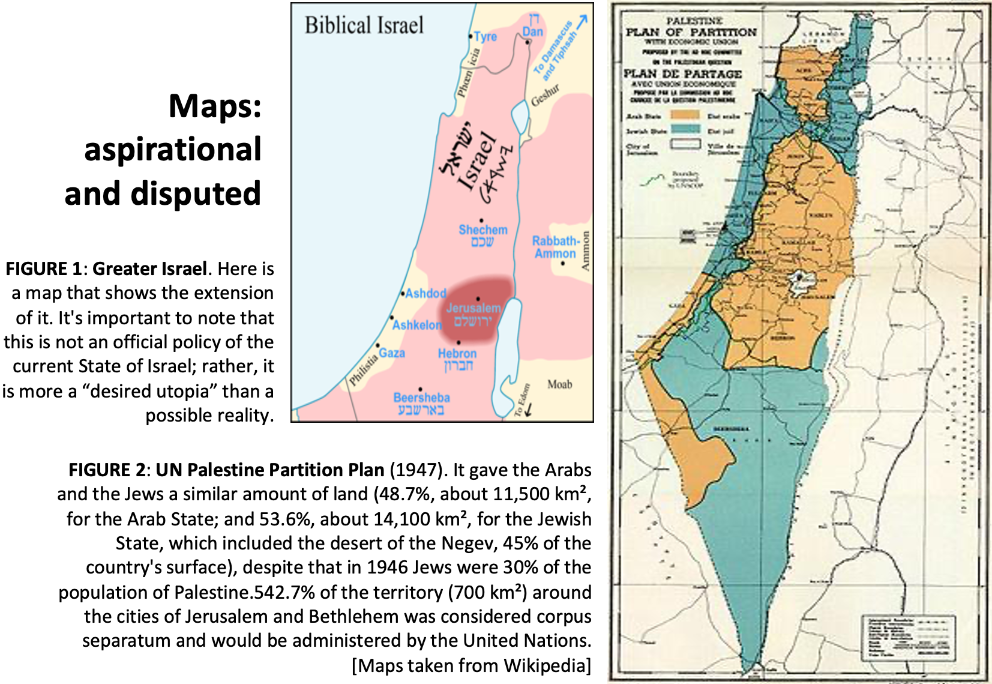
The current state of Israel, founded in 1948 with the partition of the British Protectorate of Palestine, argues its existence in the need for a Jewish state that not only represents and welcomes such a community but also meets its own religious requirements, since in Judaism the Hebrew is spoken as the “chosen people of God”, and Israel as its “Promised Land”. So, being the state of Israel the direct heir of the ancient Hebrew people, it would become the legitimate occupier of the lands quoted in Genesis 15: 18-21. This is known as the concept of Greater Israel (see map)[2].
On the Palestinian side, they exhibit as their main argument thirteen centuries of Muslim rule (638-1920) over the region of Palestine, from the Orthodox caliphate to the Ottoman Empire. They claim that the Jewish presence in the region is primarily based on the massive immigration of Jews during the late 19th and 20th centuries, following the popularization of Zionism, as well as on the expulsion of more than 700,000 Palestinians before, during and after the Arab-Israeli war of 1948, a fact known as the Nakba[3], and of many other Palestinians and Muslims in general since the beginning of the conflict. Some also base their historical claim on their origin as descendants of the Philistines.
However, although these arguments are weak, beyond historical conjecture, the reality is, nonetheless, that these aspirations have been the ones that have provoked the Palestinian-Israeli conflict. This properly begins in the early 20th century, with the rise of Zionism in response to the growing anti-Semitism in Europe, and the Arab refusal to see Jews settled in the area of Palestine. During the years of the British Mandate for Palestine (1920-1948) there were the first episodes of great violence between Jews and Palestinians. Small terrorist actions by the Arabs against Kibbutzim, which were contested by Zionist organizations, became the daily norm. This turned into a spiral of violence and assassinations, with brutal episodes such as the Buraq and Hebron revolts, which ended with some 200 Jews killed by Arabs, and some 120 Arabs killed by the British army.[4]
Another dark episode of this time was the complicit relations between the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, Haj Almin Al-Husseini, and the Nazi regime, united by a common agenda regarding Jews. He had meetings with Adolf Hitler and gave them mutual support, as the extracts of their conversations collect[5]. But it will not be until the adoption of the “United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine” through Resolution 181 (II) of the General Assembly when the war broke out on a large scale.[6] The Jews accepted the plan, but the Arab League announced that, if it became effective, they would not hesitate to invade the territory.
And so, it was. On May 14, 1948, hours after the proclamation of the state of Israel by Ben-Gurion, Israel was invaded by a joint force of Egyptian, Iraqi, Lebanese, Syrian and Jordanian troops. In this way, the 1948 Arab-Israeli War began, beginning a period of war that has not stopped until today, almost 72 years later. Despite the multiple peace agreements reached (with Egypt and Jordan), the dozens of United Nations resolutions, and the Oslo Accords, which established the roadmap for achieving a lasting peace between Israel and Palestine, conflicts continue, and they have seriously affected the development of the societies and peoples of the region.
The Israel Defense Forces
Despite the difficulties suffered since the day of its independence, Israel has managed to establish itself as the only effective democracy in the region, with a strong rule of law and a welfare state. It has a Human Development Index of 0.906, considered very high; is an example in education and development, being the third country in the world with more university graduates over the total population (20%) and is a world leader in R&D in technology. Meanwhile, the countries around it face serious difficulties, and in the case of Palestine, great misery. One of the keys to Israel's success and survival is, without a doubt, its Army. Without it, it would not have been able to lay the foundations of the country that it is today, as it would have been devastated by neighboring countries from the first day of its independence.
It is not daring to say that Israeli society is one of the most militarized in the world. It is even difficult to distinguish between Israel as a country or Israel as an army. There is no doubt that the structure of the country is based on the Army and on the concept of “one people”. The Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) act as the backbone of society and we find an overwhelming part of the country's top officials who have served as active soldiers. The paradigmatic example are the current leaders of the two main Knesset parties: Benny Ganz (former Chief of Staff of the IDF) and Benjamin Netanyahu (a veteran of the special forces in the 1970s, and combat wounded).
This influence exerted by the Tzahal[7] in the country is fundamentally due to three reasons. The first is the reality of war. Although, as we have previously commented, Israel is a prosperous country and practically equal to the rest of the western world, it lives in a reality of permanent conflict, both inside and outside its borders. When it is not carrying out large anti-terrorist operations such as Operation “Protective Edge,” carried out in Gaza in 2014, it is in an internal fight against attacks by lone wolves (especially bloody recent episodes of knife attacks on Israeli civilians and military) and against rocket and missile launches from the Gaza Strip. The Israeli population has become accustomed to the sound of missile alarms, and to seeing the “Iron Dome” anti-missile system in operation. It is common for all houses to have small air raid shelters, as well as in public buildings and schools. In them, students learn how to behave in the face of an attack and basic security measures. The vision of the Army on the street is something completely common, whether it be armored vehicles rolling through the streets, fighters flying over the sky, or platoons of soldiers getting on the public bus with their full equipment. At this point, we must not forget the suffering in which the Palestinian population constantly lives, as well as its harsh living conditions, motivated not only by the Israeli blockade, but also by living under the government of political parties such as Al-Fatah or Hamas. The reality of war is especially present in the territories under dispute with other countries: the Golan Heights in Syria and the so-called Palestinian Territories (the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip). Military operations and clashes with insurgents are practically daily in these areas.
This permanent tension and the reality of war not only affect the population indirectly, but also directly with compulsory military service. Israel is the developed country that spends the most defense budget according to its GDP and its population.[8] Today, Israel invests 4.3% of its GDP in defense (not counting investment in industry and military R&D).[9] In the early 1980s, it came to invest around 22%. Its army has 670,000 soldiers, of whom 170,000 are professionals, and 35.9% of its population (just over 3 million) are ready for combat. It is estimated that the country can carry out a general mobilization around 48-72 hours. Its military strength is based not only on its technological vanguard in terms of weapons systems such as the F-35 (and atomic arsenal), material, armored vehicles (like the Merkava MBT), but also on its compulsory military service system that keeps the majority of the population trained to defend its country. Israel has a unique military service in the western world, being compulsory for all those over 18 years of age, be they men or women. In the case of men, it lasts 32 months, while women remain under military discipline for 21 months, although those that are framed in combat units usually serve the same time as men. Military service has exceptions, such as Arabs who do not want to serve and ultra-Orthodox Jews. However, more and more Israeli Arabs serve in the armed forces, including in mixed units with Druze, Jews and Christians; the same goes for the ultra-orthodox, who are beginning to serve in units adapted to their religious needs. Citizens who complete military service remain in the reserve until they are 40 years old, although it is estimated that only a quarter of them do so actively.[10]
Social cohesion
Israeli military service and, by extension, the Israeli Defense Forces are, therefore, the greatest factor of social cohesion in the country, above even religion. This is the second reason why the army influences Israel. The experience of a country protection service carried out by all generations creates great social cohesion. In the Israeli mindset, serving in the military, protecting your family and ensuring the survival of the state is one of the greatest aspirations in life. From the school, within the academic curriculum itself, the idea of patriotism and service to the nation is integrated. And right now, despite huge contrasts between the Jewish majority and minorities, it is also a tool for social integration for Arabs, Druze and Christians. Despite racism and general mistrust towards Arabs, if you serve in the Armed Forces, the reality changes completely: you are respected, you integrate more easily into social life, and your opportunities for work and study after the enlistment period have increased considerably. Mixed units, such as Unit 585 where Bedouins and Christian Arabs serve,[11] allow these minorities to continue to throw down barriers in Israeli society, although on many occasions they find rejection from their own communities.
Israelis residing abroad are also called to service, after which many permanently settle in the country. This enhances the sense of community even for Jews still in the Diaspora.
In short, the IDF creates a sense of duty and belonging to the homeland, whatever the origin, as well as a strong link with the armed forces (which is hardly seen in other western countries) and acceptance of the sacrifices that must be made in order to ensure the survival of the country.
The third and last reason, the most important one, and the one that summarizes the role that the Army has in society and in the country, is the reality that, as said above, the survival of the country depends on the Army. This is how the military occupation of territories beyond the borders established in 1948, the bombings in civilian areas, the elimination of individual objectives are justified by the population and the Government. After 3,000 years, and since 1948 perhaps more than ever, the Israeli people depend on weapons to create a protection zone around them, and after the persecution throughout the centuries culminating in the Holocaust and its return to the “Promised Land,” neither the state nor the majority of the population are willing to yield in their security against countries or organizations that directly threaten the existence of Israel as a country. This is why despite the multiple truces and the will (political and real) to end the Arab-Israeli conflict, the country cannot afford to step back in terms of preparing its armed forces and lobbying.
Obviously, during the current Covid-19 pandemic, the Army is having a key role in the success of the country in fighting the virus. The current rate of vaccination (near 70 doses per 100 people) is boosted by the use of reserve medics from the Army, as well as the logistic experience and planning (among obviously many other factors). Also, they have provided thousands of contact tracers, and the construction of hundreds of vaccination posts, and dozens of quarantine facilities. Even could be arguable that the military training could play a role in coping with the harsh restrictions that were imposed in the country.
The State-Army-People trinity exemplifies the reality that Israel lives, where the Army has a fundamental (and difficult) role in society. It is difficult to foresee a change in reality in the near future, but without a doubt, the army will continue to have the leadership role that it has assumed, in different forms, for 3,000 years.
[1] Genesis 15:18 New International Version (NIV). 18: “On that day the Lord made a covenant with Abram and said, ‘To your descendants I give this land, from the Wadi [a] of Egypt to the great river, the Euphrates’.”
[2] Great Israel matches to previously mentioned Bible passage Gn. 15: 18-21.
[3] Independent, JS (2019, May 16). This is why Palestinians wave keys during the 'Day of Catastrophe'. Retrieved March 23, 2020, from https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/middle-east/nakba-day-catastrophe-palestinians-israel-benjamin-netanyahu-gaza-west-bank-hamas-a8346156.html
[4] Ross Stewart (2004). Causes and Consequences of the Arab-Israeli Conflict. London: Evan Brothers, Ltd., 2004.
[5] Record of the Conversation Between the Führer and the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem on November 28, 1941, in in Berlin, Documents on German Foreign Policy, 1918-1945, Series D, Vol. XIII, London , 1964, p. 881ff, in Walter Lacquer and Barry Rubin, The Israel-Arab Reader, (NY: Facts on File, 1984), pp. 79-84. Retrieved from https://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/the-mufti-and-the-f-uuml-hrer#2. “Germany stood for uncompromising war against the Jews. That naturally included active opposition to the Jewish national home in Palestine .... Germany would furnish positive and practical aid to the Arabs involved in the same struggle .... Germany's objective [is] ... solely the destruction of the Jewish element residing in the Arab sphere .... In that hour the Mufti would be the most authoritative spokesman for the Arab world. The Mufti thanked Hitler profusely. ”
[6] United Nations General Assembly A / RES / 181 (II) of 29 November 1947.
[7] Tzahal is a Hebrew acronym used to refer to the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF).
[8] Newsroom. (8th. June 2009). Arming Up: The world's biggest military spenders by population. 03-20-2020, by The Economist Retrieved from: https://www.economist.com/news/2009/06/08/arming-up
[9] Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. (nd). SIPRI Military Expenditure Database. Retrieved March 21, 2020, from https://www.sipri.org/databases/milex
[10] Gross, JA (2016, May 30). Just a quarter of all eligible reservists serve in the IDF. Retrieved March 22, 2020, from https://www.timesofisrael.com/just-a-quarter-of-all-eligible-reservists-serve-in-the-idf/
[11] AHRONHEIM, A. (2020, January 12). Arab Christians and Bedouins in the IDF: Meet the members of Unit 585. Retrieved March 19, 2020, from https://www.jpost.com/Israel-News/The-sky-is-the-limit-in-the- IDFs-unique-Unit-585-613948